Running Bitcoin: Difference between revisions
m →Sample Bitcoin.conf: update to master |
m →Sample Bitcoin.conf: update to file in current master |
||
| Line 372: | Line 372: | ||
# when the server and client are run as the same user. | # when the server and client are run as the same user. | ||
# | # | ||
# If not, you must set rpcuser and rpcpassword to secure the JSON-RPC | # If not, you must set rpcuser and rpcpassword to secure the JSON-RPC API. | ||
# | # | ||
# The | # The config option `rpcauth` can be added to server startup argument. It is set at initialization time | ||
# using the output from the script in share/rpcauth/rpcauth.py after providing a username: | # using the output from the script in share/rpcauth/rpcauth.py after providing a username: | ||
# | # | ||
| Line 416: | Line 413: | ||
# running on another host using this option: | # running on another host using this option: | ||
#rpcconnect=127.0.0.1 | #rpcconnect=127.0.0.1 | ||
# Wallet options | |||
# Create transactions that have enough fees so they are likely to begin confirmation within n blocks (default: 6). | # Create transactions that have enough fees so they are likely to begin confirmation within n blocks (default: 6). | ||
# This setting is over-ridden by the -paytxfee option. | # This setting is over-ridden by the -paytxfee option. | ||
#txconfirmtarget=n | #txconfirmtarget=n | ||
# Pay a transaction fee every time you send bitcoins. | |||
#paytxfee=0.000x | |||
# Miscellaneous options | # Miscellaneous options | ||
| Line 426: | Line 428: | ||
# both prior transactions and several dozen future transactions. | # both prior transactions and several dozen future transactions. | ||
#keypool=100 | #keypool=100 | ||
# Enable pruning to reduce storage requirements by deleting old blocks. | # Enable pruning to reduce storage requirements by deleting old blocks. | ||
Revision as of 17:59, 8 November 2018
There are two variations of the original bitcoin program available; one with a graphical user interface (usually referred to as just “Bitcoin”), and a 'headless' version (called bitcoind). They are completely compatible with each other, and take the same command-line arguments, read the same configuration file, and read and write the same data files. You can run one copy of either Bitcoin or bitcoind on your system at a time (if you accidently try to launch another, the copy will let you know that Bitcoin or bitcoind is already running and will exit).
Linux Quickstart
The simplest way to start from scratch with the command line client, automatically syncing blockchain and creating a wallet, is to just run this command (without arguments) from the directory containing your bitcoind binary:
./bitcoind
To run with the standard GUI interface:
./bitcoin-qt
Command-line arguments
These commands are accurate as of Bitcoin Core version v0.14.0.
| Command | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| -? | Print this help message and exit | |
| -version | Print version and exit | |
| -alertnotify=<cmd> | Execute command when a relevant alert is received or we see a really long fork (%s in cmd is replaced by message) | |
| -blocknotify=<cmd> | Execute command when the best block changes (%s in cmd is replaced by block hash) | |
| -assumevalid=<hex> | If this block is in the chain assume that it and its ancestors are valid and potentially skip their script verification (0 to verify all, default: 00000000000000000013176bf8d7dfeab4e1db31dc93bc311b436e82ab226b90, testnet: 00000000000128796ee387cf110ccb9d2f36cffaf7f73079c995377c65ac0dcc) | |
| -conf=<file> | Specify configuration file (default: bitcoin.conf) | |
| -datadir=<dir> | Specify data directory | |
| -dbcache=<n> | Set database cache size in megabytes (4 to 16384, default: 300) | |
| -loadblock=<file> | Imports blocks from external blk000??.dat file on startup | |
| -maxorphantx=<n> | Keep at most <n> unconnectable transactions in memory (default: 100) | |
| -maxmempool=<n> | Keep the transaction memory pool below <n> megabytes (default: 300) | |
| -mempoolexpiry=<n> | Do not keep transactions in the mempool longer than <n> hours (default: 336) | |
| -blockreconstructionextratxn=<n> | Extra transactions to keep in memory for compact block reconstructions (default: 100) | |
| -par=<n> | Set the number of script verification threads (-2 to 16, 0 = auto, <0 = leave that many cores free, default: 0) | |
| -pid=<file> | Specify pid file (default: bitcoind.pid) | |
| -prune=<n> | Reduce storage requirements by enabling pruning (deleting) of old blocks. This allows the pruneblockchain RPC to be called to delete specific blocks, and enables automatic pruning of old blocks if a target size in MiB is provided. This mode is incompatible with -txindex and -rescan. Warning: Reverting this setting requires re-downloading the entire blockchain. (default: 0 = disable pruning blocks, 1 = allow manual pruning via RPC, >550 = automatically prune block files to stay under the specified target size in MiB) | |
| -reindex-chainstate | Rebuild chain state from the currently indexed blocks | |
| -reindex | Rebuild chain state and block index from the blk*.dat files on disk | |
| -sysperms | Create new files with system default permissions, instead of umask 077 (only effective with disabled wallet functionality) | |
| -txindex | Maintain a full transaction index, used by the getrawtransaction rpc call (default: 0) | |
Connection options: | ||
| -addnode=<ip> | Add a node to connect to and attempt to keep the connection open | |
| -banscore=<n> | Threshold for disconnecting misbehaving peers (default: 100) | |
| -bantime=<n> | Number of seconds to keep misbehaving peers from reconnecting (default: 86400) | |
| -bind=<addr> | Bind to given address and always listen on it. Use [host]:port notation for IPv6 | |
| -connect=<ip> | Connect only to the specified node(s); -noconnect or -connect=0 alone to disable automatic connections | |
| -discover | Discover own IP addresses (default: 1 when listening and no -externalip or -proxy) | |
| -dns | Allow DNS lookups for -addnode, -seednode and -connect (default: 1) | |
| -dnsseed | Query for peer addresses via DNS lookup, if low on addresses (default: 1 unless -connect/-noconnect) | |
| -externalip=<ip> | Specify your own public address | |
| -forcednsseed | Always query for peer addresses via DNS lookup (default: 0) | |
| -listen | Accept connections from outside (default: 1 if no -proxy or -connect/-noconnect) | |
| -listenonion | Automatically create Tor hidden service (default: 1) | |
| -maxconnections=<n> | Maintain at most <n> connections to peers (default: 125) | |
| -maxreceivebuffer=<n> | Maximum per-connection receive buffer, <n>*1000 bytes (default: 5000) | |
| -maxsendbuffer=<n> | Maximum per-connection send buffer, <n>*1000 bytes (default: 1000) | |
| -maxtimeadjustment | Maximum allowed median peer time offset adjustment. Local perspective of time may be influenced by peers forward or backward by this amount. (default: 4200 seconds) | |
| -onion=<ip:port> | Use separate SOCKS5 proxy to reach peers via Tor hidden services (default: -proxy) | |
| -onlynet=<net> | Only connect to nodes in network <net> (ipv4, ipv6 or onion) | |
| -permitbaremultisig | Relay non-P2SH multisig (default: 1) | |
| -peerbloomfilters | Support filtering of blocks and transaction with bloom filters (default: 1) | |
| -port=<port> | Listen for connections on <port> (default: 8333 or testnet: 18333) | |
| -proxy=<ip:port> | Connect through SOCKS5 proxy | |
| -proxyrandomize | Randomize credentials for every proxy connection. This enables Tor stream isolation (default: 1) | |
| -rpcserialversion | Sets the serialization of raw transaction or block hex returned in non-verbose mode, non-segwit(0) or segwit(1) (default: 1) | |
| -seednode=<ip> | Connect to a node to retrieve peer addresses, and disconnect | |
| -timeout=<n> | Specify connection timeout in milliseconds (minimum: 1, default: 5000) | |
| -torcontrol=<ip>:<port> | Tor control port to use if onion listening enabled (default: 127.0.0.1:9051) | |
| -torpassword=<pass> | Tor control port password (default: empty) | |
| -upnp=<pass> | Use UPnP to map the listening port (default: 0) | |
| -whitebind=<addr> | Bind to given address and whitelist peers connecting to it. Use [host]:port notation for IPv6 | |
| -whitelist=<IP address or network> | Whitelist peers connecting from the given IP address (e.g. 1.2.3.4) or CIDR notated network (e.g. 1.2.3.0/24). Can be specified multiple times. Whitelisted peers cannot be DoS banned and their transactions are always relayed, even if they are already in the mempool, useful e.g. for a gateway | |
| -whitelistrelay | Accept relayed transactions received from whitelisted peers even when not relaying transactions (default: 1) | |
| -whitelistforcerelay | Force relay of transactions from whitelisted peers even if they violate local relay policy (default: 1) | |
| -maxuploadtarget=<n> | Tries to keep outbound traffic under the given target (in MiB per 24h), 0 = no limit (default: 0) | |
Wallet options: | ||
| -disablewallet | Do not load the wallet and disable wallet RPC calls | |
| -keypool=<n> | Set key pool size to <n> (default: 100) | |
| -fallbackfee=<amt> | A fee rate (in BTC/kB) that will be used when fee estimation has insufficient data (default: 0.0002) | |
| -mintxfee=<amt> | Fees (in BTC/kB) smaller than this are considered zero fee for transaction creation (default: 0.00001) | |
| -paytxfee=<amt> | Fee (in BTC/kB) to add to transactions you send (default: 0.00) | |
| -rescan | Rescan the block chain for missing wallet transactions on startup | |
| -salvagewallet | Attempt to recover private keys from a corrupt wallet on startup | |
| -spendzeroconfchange | Spend unconfirmed change when sending transactions (default: 1) | |
| -txconfirmtarget=<n> | If paytxfee is not set, include enough fee so transactions begin confirmation on average within n blocks (default: 6) | |
| -usehd | Use hierarchical deterministic key generation (HD) after BIP32. Only has effect during wallet creation/first start (default: 1) | |
| -walletrbf | Send transactions with full-RBF opt-in enabled (default: 0) | |
| -upgradewallet | Upgrade wallet to latest format on startup | |
| -wallet=<file> | Specify wallet file (within data directory) (default: wallet.dat) | |
| -walletbroadcast | Make the wallet broadcast transactions (default: 1) | |
| -walletnotify=<cmd> | Execute command when a wallet transaction changes (%s in cmd is replaced by TxID) | |
| -zapwallettxes=<mode> | Delete all wallet transactions and only recover those parts of the blockchain through -rescan on startup (1 = keep tx meta data e.g. account owner and payment request information, 2 = drop tx meta data) | |
ZeroMQ notification options: | ||
| -zmqpubhashblock=<address> | Enable publish hash block in <address> | |
| -zmqpubhashtx=<address> | Enable publish hash transaction in <address> | |
| -zmqpubrawblock=<address> | Enable publish raw block in <address> | |
| -zmqpubrawtx=<address> | Enable publish raw transaction in <address> | |
Debugging/Testing options: | ||
| -uacomment=<cmt> | Append comment to the user agent string | |
| -debug=<category> | Output debugging information (default: 0, supplying <category> is optional). If <category> is not supplied or if <category> = 1, output all debugging information.<category> can be: addrman, alert, bench, cmpctblock, coindb, db, http, libevent, lock, mempool, mempoolrej, net, proxy, prune, rand, reindex, rpc, selectcoins, tor, zmq, qt. | |
| -help-debug | Show all debugging options (usage: --help -help-debug) | |
| -logips | Include IP addresses in debug output (default: 0) | |
| -logtimestamps | Prepend debug output with timestamp (default: 1) | |
| -minrelaytxfee=<amt> | Fees (in BTC/kB) smaller than this are considered zero fee for relaying, mining and transaction creation (default: 0.00001) | |
| -maxtxfee=<amt> | Maximum total fees (in BTC) to use in a single wallet transaction or raw transaction; setting this too low may abort large transactions (default: 0.10) | |
| -printtoconsole | Send trace/debug info to console instead of debug.log file | |
| -shrinkdebugfile | Shrink debug.log file on client startup (default: 1 when no -debug) | |
Chain selection options: | ||
| -testnet | Use the test chain | |
Node relay options: | ||
| -bytespersigop | Equivalent bytes per sigop in transactions for relay and mining (default: 20) | |
| -datacarrier | Relay and mine data carrier transactions (default: 1) | |
| -datacarriersize | Maximum size of data in data carrier transactions we relay and mine (default: 83) | |
| -mempoolreplacement | Enable transaction replacement in the memory pool (default: 1) | |
Block creation options: | ||
| -blockmaxweight=<n> | Set maximum BIP141 block weight (default: 3000000) | |
| -blockmaxsize=<n> | Set maximum block size in bytes (default: 750000) | |
| -blockprioritysize=<n> | Set maximum size of high-priority/low-fee transactions in bytes (default: 0) | |
| -blockmintxfee=<amt> | Set lowest fee rate (in BTC/kB) for transactions to be included in block creation. (default: 0.00001) | |
RPC server options: | ||
| -server | Accept command line and JSON-RPC commands | |
| -rest | Accept public REST requests (default: 0) | |
| -rpcbind=<addr> | Bind to given address to listen for JSON-RPC connections. Use [host]:port notation for IPv6. This option can be specified multiple times (default: bind to all interfaces) | |
| -rpccookiefile=<loc> | Location of the auth cookie (default: data dir) | |
| -rpcuser=<user> | Username for JSON-RPC connections | |
| -rpcpassword=<pw> | Password for JSON-RPC connections | |
| -rpcauth=<userpw> | Username and hashed password for JSON-RPC connections. The field <userpw> comes in the format: <USERNAME>:<SALT>$<HASH>. A canonical python script is included in share/rpcuser. The client then connects normally using the rpcuser=<USERNAME>/rpcpassword=<PASSWORD> pair of arguments. This option can be specified multiple times | |
| -rpcport=<port> | Listen for JSON-RPC connections on <port> (default: 8332 or testnet: 18332) | |
| -rpcallowip=<ip> | Allow JSON-RPC connections from specified source. Valid for <ip> are a single IP (e.g. 1.2.3.4), a network/netmask (e.g. 1.2.3.4/255.255.255.0) or a network/CIDR (e.g. 1.2.3.4/24). This option can be specified multiple times | |
| -rpcthreads=<n> | Set the number of threads to service RPC calls (default: 4) | |
UI Options: | ||
| -choosedatadir | Choose data directory on startup (default: 0) | |
| -lang=<lang> | Set language, for example "de_DE" (default: system locale) | |
| -min | Start minimized | |
| -rootcertificates=<file> | Set SSL root certificates for payment request (default: -system-) | |
| -splash | Show splash screen on startup (default: 1) | |
| -resetguisettings | Reset all settings changed in the GUI | |
Many of the boolean options can also be set to off by specifying them with a "no" prefix: e.g. -nodnseed.
Bitcoin.conf Configuration File
All command-line options (except for -conf) may be specified in a configuration file, and all configuration file options may also be specified on the command line. Command-line options override values set in the configuration file.
The configuration file is a list of setting=value pairs, one per line, with optional comments starting with the '#' character.
The configuration file is not automatically created; you can create it using your favorite plain-text editor. A user-friendly configuration file generator is available here. By default, Bitcoin (or bitcoind) will look for a file named 'bitcoin.conf' in the bitcoin data directory, but both the data directory and the configuration file path may be changed using the -datadir and -conf command-line arguments.
| Operating System | Default bitcoin datadir | Typical path to configuration file |
|---|---|---|
| Windows | %APPDATA%\Bitcoin\ | C:\Users\username\AppData\Roaming\Bitcoin\bitcoin.conf |
| Linux | $HOME/.bitcoin/ | /home/username/.bitcoin/bitcoin.conf |
| Mac OSX | $HOME/Library/Application Support/Bitcoin/ | /Users/username/Library/Application Support/Bitcoin/bitcoin.conf |
Note: if running Bitcoin in testnet mode, the sub-folder "testnet" will be appended to the data directory automatically.
Sample Bitcoin.conf
Copied from https://github.com/bitcoin/bitcoin/blob/master/share/examples/bitcoin.conf:
## ## bitcoin.conf configuration file. Lines beginning with # are comments. ## # Network-related settings: # Run on the test network instead of the real bitcoin network. #testnet=0 # Run a regression test network #regtest=0 # Connect via a SOCKS5 proxy #proxy=127.0.0.1:9050 # Bind to given address and always listen on it. Use [host]:port notation for IPv6 #bind=<addr> # Bind to given address and whitelist peers connecting to it. Use [host]:port notation for IPv6 #whitebind=<addr> ############################################################## ## Quick Primer on addnode vs connect ## ## Let's say for instance you use addnode=4.2.2.4 ## ## addnode will connect you to and tell you about the ## ## nodes connected to 4.2.2.4. In addition it will tell ## ## the other nodes connected to it that you exist so ## ## they can connect to you. ## ## connect will not do the above when you 'connect' to it. ## ## It will *only* connect you to 4.2.2.4 and no one else.## ## ## ## So if you're behind a firewall, or have other problems ## ## finding nodes, add some using 'addnode'. ## ## ## ## If you want to stay private, use 'connect' to only ## ## connect to "trusted" nodes. ## ## ## ## If you run multiple nodes on a LAN, there's no need for ## ## all of them to open lots of connections. Instead ## ## 'connect' them all to one node that is port forwarded ## ## and has lots of connections. ## ## Thanks goes to [Noodle] on Freenode. ## ############################################################## # Use as many addnode= settings as you like to connect to specific peers #addnode=69.164.218.197 #addnode=10.0.0.2:8333 # Alternatively use as many connect= settings as you like to connect ONLY to specific peers #connect=69.164.218.197 #connect=10.0.0.1:8333 # Listening mode, enabled by default except when 'connect' is being used #listen=1 # Maximum number of inbound+outbound connections. #maxconnections= # # JSON-RPC options (for controlling a running Bitcoin/bitcoind process) # # server=1 tells Bitcoin-Qt and bitcoind to accept JSON-RPC commands #server=0 # Bind to given address to listen for JSON-RPC connections. Use [host]:port notation for IPv6. # This option can be specified multiple times (default: bind to all interfaces) #rpcbind=<addr> # If no rpcpassword is set, rpc cookie auth is sought. The default `-rpccookiefile` name # is .cookie and found in the `-datadir` being used for bitcoind. This option is typically used # when the server and client are run as the same user. # # If not, you must set rpcuser and rpcpassword to secure the JSON-RPC API. # # The config option `rpcauth` can be added to server startup argument. It is set at initialization time # using the output from the script in share/rpcauth/rpcauth.py after providing a username: # # ./share/rpcauth/rpcauth.py alice # String to be appended to bitcoin.conf: # rpcauth=alice:f7efda5c189b999524f151318c0c86$d5b51b3beffbc02b724e5d095828e0bc8b2456e9ac8757ae3211a5d9b16a22ae # Your password: # DONT_USE_THIS_YOU_WILL_GET_ROBBED_8ak1gI25KFTvjovL3gAM967mies3E= # # On client-side, you add the normal user/password pair to send commands: #rpcuser=alice #rpcpassword=DONT_USE_THIS_YOU_WILL_GET_ROBBED_8ak1gI25KFTvjovL3gAM967mies3E= # # You can even add multiple entries of these to the server conf file, and client can use any of them: # rpcauth=bob:b2dd077cb54591a2f3139e69a897ac$4e71f08d48b4347cf8eff3815c0e25ae2e9a4340474079f55705f40574f4ec99 # How many seconds bitcoin will wait for a complete RPC HTTP request. # after the HTTP connection is established. #rpcclienttimeout=30 # By default, only RPC connections from localhost are allowed. # Specify as many rpcallowip= settings as you like to allow connections from other hosts, # either as a single IPv4/IPv6 or with a subnet specification. # NOTE: opening up the RPC port to hosts outside your local trusted network is NOT RECOMMENDED, # because the rpcpassword is transmitted over the network unencrypted. # server=1 tells Bitcoin-Qt to accept JSON-RPC commands. # it is also read by bitcoind to determine if RPC should be enabled #rpcallowip=10.1.1.34/255.255.255.0 #rpcallowip=1.2.3.4/24 #rpcallowip=2001:db8:85a3:0:0:8a2e:370:7334/96 # Listen for RPC connections on this TCP port: #rpcport=8332 # You can use Bitcoin or bitcoind to send commands to Bitcoin/bitcoind # running on another host using this option: #rpcconnect=127.0.0.1 # Wallet options # Create transactions that have enough fees so they are likely to begin confirmation within n blocks (default: 6). # This setting is over-ridden by the -paytxfee option. #txconfirmtarget=n # Pay a transaction fee every time you send bitcoins. #paytxfee=0.000x # Miscellaneous options # Pre-generate this many public/private key pairs, so wallet backups will be valid for # both prior transactions and several dozen future transactions. #keypool=100 # Enable pruning to reduce storage requirements by deleting old blocks. # This mode is incompatible with -txindex and -rescan. # 0 = default (no pruning). # 1 = allows manual pruning via RPC. # >=550 = target to stay under in MiB. #prune=550 # User interface options # Start Bitcoin minimized #min=1 # Minimize to the system tray #minimizetotray=1
Platforms
Windows
Start automatically
To configure the Bitcoin client to start automatically:
You might use the configuration-file, or the GUI-Settings:
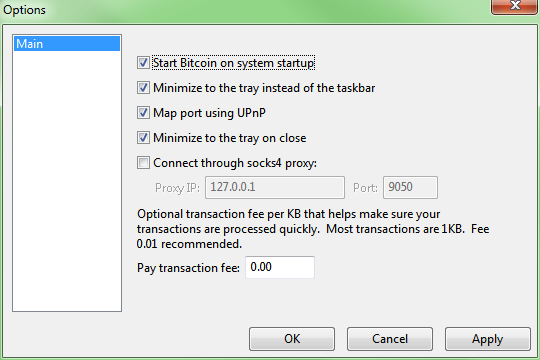
Settings -> Options
then mark the checkbox titled:
[X] Start Bitcoin on system startup
Batch automation
To work with batch, you have to start the daemon (bitcoind.exe). The bitcoin.exe run with option "-server" will respond with GUI-messages you are not able to process its answers.
Mac
Linux
See Also
| |||||||||||