OP CHECKSIG: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
this sentence is completely misleading. |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
# the public key and the signature are popped from the stack, in that order. | # the public key and the signature are popped from the stack, in that order. | ||
# A new subscript is created from the instruction from the most recently parsed OP_CODESEPARATOR (last one in script) to the end of the script. If there is no OP_CODESEPARATOR the entire script becomes the subscript (hereby referred to as subScript) | # A new subscript is created from the instruction from the most recently parsed OP_CODESEPARATOR (last one in script) to the end of the script. If there is no OP_CODESEPARATOR the entire script becomes the subscript (hereby referred to as subScript) | ||
# The sig is deleted from subScript | # The sig is deleted from subScript. | ||
# All OP_CODESEPARATORS are removed from subScript | # All OP_CODESEPARATORS are removed from subScript | ||
# The hashtype is removed from the last byte of the sig and stored | # The hashtype is removed from the last byte of the sig and stored | ||
Revision as of 13:13, 5 November 2011
OP_CHECKSIG is script opcode used to verify that the signature for a tx input is valid. OP_CHECKSIG expects two values to be on the stack, these are, in order of stack depth, the public key and the signature of the script. These two values are normally obtained by running the scriptSig script of the transaction input we are attempting to validate. After the scriptSig script is run the script is deleted but the stack is left as is, and then then scriptPubKey script from the previous transaction output that is now being spent is run, generally concluding in an OP_CHECKSIG.
The standard scriptPubKey checks that the public key (actually a hash of) is a particular value, and that OP_CHECKSIG passes.
For normal transaction inputs if the creator of the current transaction can successfully create a ScriptSig signature that uses the right public key for the ScriptPubKey of the transaction output they are attempting to spend, that transaction input is considered valid.
Parameters
In addition to the script code itself and the stack parameters, to operate OP_CHECKSIG needs to know the current transaction, the current transaction input, and the current hashtype (discussed later)
How it works
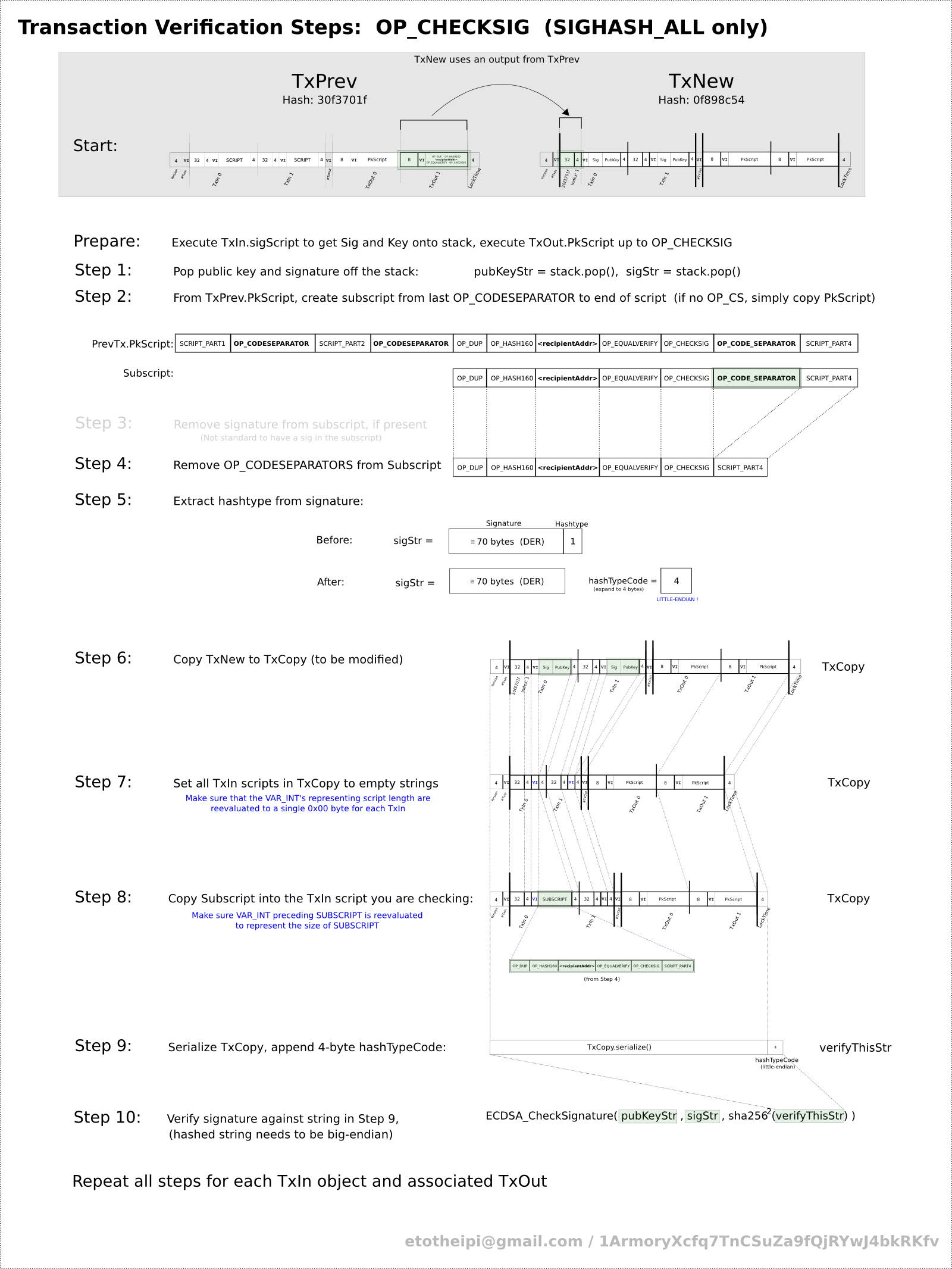
- the public key and the signature are popped from the stack, in that order.
- A new subscript is created from the instruction from the most recently parsed OP_CODESEPARATOR (last one in script) to the end of the script. If there is no OP_CODESEPARATOR the entire script becomes the subscript (hereby referred to as subScript)
- The sig is deleted from subScript.
- All OP_CODESEPARATORS are removed from subScript
- The hashtype is removed from the last byte of the sig and stored
- A deep copy is made of the current transaction (hereby referred to txCopy)
- The scripts for all transaction inputs in txCopy are set to empty scripts
- The script for the current transaction input in txCopy is set to subScript
Now depending on the hashtype various things can happen to txCopy, these will be discussed individually
Hashtype Values (from script.h):
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| SIGHASH_ALL | 0x00000001 |
| SIGHASH_NONE | 0x00000002 |
| SIGHASH_SINGLE | 0x00000003 |
| SIGHASH_ANYONECANPAY | 0x00000080 |
Hashtype SIGHASH_ALL (default)
No special handling occurs in the default case
Hashtype SIGHASH_NONE
- The output of txCopy is set to a vector of zero size.
- All other inputs aside from the current input in txCopy have their nSequence index set to zero
Hashtype SIGHASH_SINGLE
- The output of txCopy is resized to the size of the current input index+1
- All other txCopy outputs aside from the output that is the same as the current input index are set to a blank script and a value of (long) -1;
- All other txCopy inputs aside from the current input are set to have an nSequence index of zero
Hashtype SIGHASH_ANYONECANPAY
- The txCopy input vector is resized to a length of one
- The current input is set as the first and only member of this vector
Final signature
An array of bytes is constructed from the serialized txCopy + four bytes for the hash type. This array is sha256 hashed twice, then the public key is used to to check the supplied signature against the hash.
Return values
OP_CHECKSIG will push true to the stack if the check passed, false otherwise. OP_CHECKSIG_VERIFY leaves nothing on the stack but will cause the script eval to fail immediately if the check does not pass.
Code samples and raw dumps
Taking the first transaction in Bitcoin which is in block number 170, we would get after serialising the transaction but before we hash+sign (or verify) it:
- http://blockexplorer.com/block/00000000d1145790a8694403d4063f323d499e655c83426834d4ce2f8dd4a2ee
- http://blockexplorer.com/tx/f4184fc596403b9d638783cf57adfe4c75c605f6356fbc91338530e9831e9e16
See also libbitcoin for code samples.
01 00 00 00 version 01 number of inputs (var_uint) input 0: c9 97 a5 e5 6e 10 41 02 input address hash fa 20 9c 6a 85 2d d9 06 60 a2 0b 2d 9c 35 24 23 ed ce 25 85 7f cd 37 04 00 00 00 00 input index 43 size of script (var_uint) 41 push 65 bytes to stack 04 11 db 93 e1 dc db 8a 01 6b 49 84 0f 8c 53 bc 1e b6 8a 38 2e 97 b1 48 2e ca d7 b1 48 a6 90 9a 5c b2 e0 ea dd fb 84 cc f9 74 44 64 f8 2e 16 0b fa 9b 8b 64 f9 d4 c0 3f 99 9b 86 43 f6 56 b4 12 a3 ac OP_CHECKSIG ff ff ff ff sequence 02 number of outputs (var_uint) output 0: 00 ca 9a 3b 00 00 00 00 amount = 10.00000000 43 size of script (var_uint) script for output 0: 41 push 65 bytes to stack 04 ae 1a 62 fe 09 c5 f5 1b 13 90 5f 07 f0 6b 99 a2 f7 15 9b 22 25 f3 74 cd 37 8d 71 30 2f a2 84 14 e7 aa b3 73 97 f5 54 a7 df 5f 14 2c 21 c1 b7 30 3b 8a 06 26 f1 ba de d5 c7 2a 70 4f 7e 6c d8 4c ac OP_CHECKSIG output 1: 00 28 6b ee 00 00 00 00 amount = 40.00000000 43 size of script (var_uint) script for output 1: 41 push 65 bytes to stack 04 11 db 93 e1 dc db 8a 01 6b 49 84 0f 8c 53 bc 1e b6 8a 38 2e 97 b1 48 2e ca d7 b1 48 a6 90 9a 5c b2 e0 ea dd fb 84 cc f9 74 44 64 f8 2e 16 0b fa 9b 8b 64 f9 d4 c0 3f 99 9b 86 43 f6 56 b4 12 a3 ac OP_CHECKSIG 00 00 00 00 locktime 01 00 00 00 hash_code_type (added on) result = 01 00 00 00 01 c9 97 a5 e5 6e 10 41 02 fa 20 9c 6a 85 2d d9 06 60 a2 0b 2d 9c 35 24 23 ed ce 25 85 7f cd 37 04 00 00 00 00 43 41 04 11 db 93 e1 dc db 8a 01 6b 49 84 0f 8c 53 bc 1e b6 8a 38 2e 97 b1 48 2e ca d7 b1 48 a6 90 9a 5c b2 e0 ea dd fb 84 cc f9 74 44 64 f8 2e 16 0b fa 9b 8b 64 f9 d4 c0 3f 99 9b 86 43 f6 56 b4 12 a3 ac ff ff ff ff 02 00 ca 9a 3b 00 00 00 00 43 41 04 ae 1a 62 fe 09 c5 f5 1b 13 90 5f 07 f0 6b 99 a2 f7 15 9b 22 25 f3 74 cd 37 8d 71 30 2f a2 84 14 e7 aa b3 73 97 f5 54 a7 df 5f 14 2c 21 c1 b7 30 3b 8a 06 26 f1 ba de d5 c7 2a 70 4f 7e 6c d8 4c ac 00 28 6b ee 00 00 00 00 43 41 04 11 db 93 e1 dc db 8a 01 6b 49 84 0f 8c 53 bc 1e b6 8a 38 2e 97 b1 48 2e ca d7 b1 48 a6 90 9a 5c b2 e0 ea dd fb 84 cc f9 74 44 64 f8 2e 16 0b fa 9b 8b 64 f9 d4 c0 3f 99 9b 86 43 f6 56 b4 12 a3 ac 00 00 00 00 01 00 00 00
To understand where that raw dump has come from, it may be useful to examine tests/ec-key.cpp in libbitcoin,
libbitcoin has a unit test under tests/ec-key.cpp (make ec-key && ./bin/tests/ec-key). There is also a working OP_CHECKSIG implementation in src/script.cpp under script::op_checksig(). See also the unit test: tests/script-test.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <bitcoin/util/serializer.hpp>
#include <bitcoin/util/elliptic_curve_key.hpp>
#include <bitcoin/util/sha256.hpp>
#include <bitcoin/util/assert.hpp>
#include <bitcoin/util/logger.hpp>
#include <bitcoin/types.hpp>
#include <openssl/ecdsa.h>
#include <openssl/obj_mac.h>
using libbitcoin::elliptic_curve_key;
using libbitcoin::serializer;
using libbitcoin::hash_digest;
using libbitcoin::data_chunk;
using libbitcoin::log_info;
using libbitcoin::log_fatal;
int main()
{
serializer ss;
// blk number 170, tx 1, input 0
// version = 1
ss.write_4_bytes(1);
// 1 inputs
ss.write_var_uint(1);
// input 0
// prevout hash
ss.write_hash(hash_digest{0x04, 0x37, 0xcd, 0x7f, 0x85, 0x25, 0xce, 0xed, 0x23, 0x24, 0x35, 0x9c, 0x2d, 0x0b, 0xa2, 0x60, 0x06, 0xd9, 0x2d, 0x85, 0x6a, 0x9c, 0x20, 0xfa, 0x02, 0x41, 0x10, 0x6e, 0xe5, 0xa5, 0x97, 0xc9});
// prevout index
ss.write_4_bytes(0);
// input script after running OP_CHECKSIG for this tx is a single
// OP_CHECKSIG opcode
data_chunk raw_data;
raw_data = {0x04, 0x11, 0xdb, 0x93, 0xe1, 0xdc, 0xdb, 0x8a, 0x01, 0x6b, 0x49, 0x84, 0x0f, 0x8c, 0x53, 0xbc, 0x1e, 0xb6, 0x8a, 0x38, 0x2e, 0x97, 0xb1, 0x48, 0x2e, 0xca, 0xd7, 0xb1, 0x48, 0xa6, 0x90, 0x9a, 0x5c, 0xb2, 0xe0, 0xea, 0xdd, 0xfb, 0x84, 0xcc, 0xf9, 0x74, 0x44, 0x64, 0xf8, 0x2e, 0x16, 0x0b, 0xfa, 0x9b, 0x8b, 0x64, 0xf9, 0xd4, 0xc0, 0x3f, 0x99, 0x9b, 0x86, 0x43, 0xf6, 0x56, 0xb4, 0x12, 0xa3};
data_chunk raw_script;
raw_script = data_chunk();
raw_script.push_back(raw_data.size());
libbitcoin::extend_data(raw_script, raw_data);
raw_script.push_back(172);
ss.write_var_uint(raw_script.size());
ss.write_data(raw_script);
// sequence
ss.write_4_bytes(0xffffffff);
// 2 outputs for this tx
ss.write_var_uint(2);
// output 0
ss.write_8_bytes(1000000000);
// script for output 0
raw_data = {0x04, 0xae, 0x1a, 0x62, 0xfe, 0x09, 0xc5, 0xf5, 0x1b, 0x13, 0x90, 0x5f, 0x07, 0xf0, 0x6b, 0x99, 0xa2, 0xf7, 0x15, 0x9b, 0x22, 0x25, 0xf3, 0x74, 0xcd, 0x37, 0x8d, 0x71, 0x30, 0x2f, 0xa2, 0x84, 0x14, 0xe7, 0xaa, 0xb3, 0x73, 0x97, 0xf5, 0x54, 0xa7, 0xdf, 0x5f, 0x14, 0x2c, 0x21, 0xc1, 0xb7, 0x30, 0x3b, 0x8a, 0x06, 0x26, 0xf1, 0xba, 0xde, 0xd5, 0xc7, 0x2a, 0x70, 0x4f, 0x7e, 0x6c, 0xd8, 0x4c};
// when data < 75, we can just write it's length as a single byte ('special'
// opcodes)
raw_script = data_chunk();
raw_script.push_back(raw_data.size());
libbitcoin::extend_data(raw_script, raw_data);
// OP_CHECKSIG
raw_script.push_back(172);
// now actually write the script
ss.write_var_uint(raw_script.size());
ss.write_data(raw_script);
// output 0
ss.write_8_bytes(4000000000);
// script for output 0
raw_data = {0x04, 0x11, 0xdb, 0x93, 0xe1, 0xdc, 0xdb, 0x8a, 0x01, 0x6b, 0x49, 0x84, 0x0f, 0x8c, 0x53, 0xbc, 0x1e, 0xb6, 0x8a, 0x38, 0x2e, 0x97, 0xb1, 0x48, 0x2e, 0xca, 0xd7, 0xb1, 0x48, 0xa6, 0x90, 0x9a, 0x5c, 0xb2, 0xe0, 0xea, 0xdd, 0xfb, 0x84, 0xcc, 0xf9, 0x74, 0x44, 0x64, 0xf8, 0x2e, 0x16, 0x0b, 0xfa, 0x9b, 0x8b, 0x64, 0xf9, 0xd4, 0xc0, 0x3f, 0x99, 0x9b, 0x86, 0x43, 0xf6, 0x56, 0xb4, 0x12, 0xa3};
// when data < 75, we can just write it's length as a single byte ('special'
raw_script.push_back(raw_data.size());
libbitcoin::extend_data(raw_script, raw_data);
// OP_CHECKSIG
raw_script.push_back(172);
// now actually write the script
ss.write_var_uint(raw_script.size());
ss.write_data(raw_script);
// End of 2 outputs
// locktime
ss.write_4_bytes(0);
// write hash_type_code
ss.write_4_bytes(1);
// Dump hex to screen
log_info() << "hashing:";
{
auto log_obj = log_info();
log_obj << std::hex;
for (int val: ss.get_data())
log_obj << std::setfill('0') << std::setw(2) << val << ' ';
}
log_info();
data_chunk raw_tx = {0x01, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x01, 0xc9, 0x97, 0xa5, 0xe5, 0x6e, 0x10, 0x41, 0x02, 0xfa, 0x20, 0x9c, 0x6a, 0x85, 0x2d, 0xd9, 0x06, 0x60, 0xa2, 0x0b, 0x2d, 0x9c, 0x35, 0x24, 0x23, 0xed, 0xce, 0x25, 0x85, 0x7f, 0xcd, 0x37, 0x04, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x43, 0x41, 0x04, 0x11, 0xdb, 0x93, 0xe1, 0xdc, 0xdb, 0x8a, 0x01, 0x6b, 0x49, 0x84, 0x0f, 0x8c, 0x53, 0xbc, 0x1e, 0xb6, 0x8a, 0x38, 0x2e, 0x97, 0xb1, 0x48, 0x2e, 0xca, 0xd7, 0xb1, 0x48, 0xa6, 0x90, 0x9a, 0x5c, 0xb2, 0xe0, 0xea, 0xdd, 0xfb, 0x84, 0xcc, 0xf9, 0x74, 0x44, 0x64, 0xf8, 0x2e, 0x16, 0x0b, 0xfa, 0x9b, 0x8b, 0x64, 0xf9, 0xd4, 0xc0, 0x3f, 0x99, 0x9b, 0x86, 0x43, 0xf6, 0x56, 0xb4, 0x12, 0xa3, 0xac, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0x02, 0x00, 0xca, 0x9a, 0x3b, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x43, 0x41, 0x04, 0xae, 0x1a, 0x62, 0xfe, 0x09, 0xc5, 0xf5, 0x1b, 0x13, 0x90, 0x5f, 0x07, 0xf0, 0x6b, 0x99, 0xa2, 0xf7, 0x15, 0x9b, 0x22, 0x25, 0xf3, 0x74, 0xcd, 0x37, 0x8d, 0x71, 0x30, 0x2f, 0xa2, 0x84, 0x14, 0xe7, 0xaa, 0xb3, 0x73, 0x97, 0xf5, 0x54, 0xa7, 0xdf, 0x5f, 0x14, 0x2c, 0x21, 0xc1, 0xb7, 0x30, 0x3b, 0x8a, 0x06, 0x26, 0xf1, 0xba, 0xde, 0xd5, 0xc7, 0x2a, 0x70, 0x4f, 0x7e, 0x6c, 0xd8, 0x4c, 0xac, 0x00, 0x28, 0x6b, 0xee, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x43, 0x41, 0x04, 0x11, 0xdb, 0x93, 0xe1, 0xdc, 0xdb, 0x8a, 0x01, 0x6b, 0x49, 0x84, 0x0f, 0x8c, 0x53, 0xbc, 0x1e, 0xb6, 0x8a, 0x38, 0x2e, 0x97, 0xb1, 0x48, 0x2e, 0xca, 0xd7, 0xb1, 0x48, 0xa6, 0x90, 0x9a, 0x5c, 0xb2, 0xe0, 0xea, 0xdd, 0xfb, 0x84, 0xcc, 0xf9, 0x74, 0x44, 0x64, 0xf8, 0x2e, 0x16, 0x0b, 0xfa, 0x9b, 0x8b, 0x64, 0xf9, 0xd4, 0xc0, 0x3f, 0x99, 0x9b, 0x86, 0x43, 0xf6, 0x56, 0xb4, 0x12, 0xa3, 0xac, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x01, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00};
BITCOIN_ASSERT(raw_tx == ss.get_data());
hash_digest tx_hash = libbitcoin::generate_sha256_hash(ss.get_data());
data_chunk pubkey{0x04, 0x11, 0xdb, 0x93, 0xe1, 0xdc, 0xdb, 0x8a, 0x01, 0x6b, 0x49, 0x84, 0x0f, 0x8c, 0x53, 0xbc, 0x1e, 0xb6, 0x8a, 0x38, 0x2e, 0x97, 0xb1, 0x48, 0x2e, 0xca, 0xd7, 0xb1, 0x48, 0xa6, 0x90, 0x9a, 0x5c, 0xb2, 0xe0, 0xea, 0xdd, 0xfb, 0x84, 0xcc, 0xf9, 0x74, 0x44, 0x64, 0xf8, 0x2e, 0x16, 0x0b, 0xfa, 0x9b, 0x8b, 0x64, 0xf9, 0xd4, 0xc0, 0x3f, 0x99, 0x9b, 0x86, 0x43, 0xf6, 0x56, 0xb4, 0x12, 0xa3};
// Leave out last byte since that's the hash_type_code (SIGHASH_ALL in this
// case)
data_chunk signature{0x30, 0x44, 0x02, 0x20, 0x4e, 0x45, 0xe1, 0x69, 0x32, 0xb8, 0xaf, 0x51, 0x49, 0x61, 0xa1, 0xd3, 0xa1, 0xa2, 0x5f, 0xdf, 0x3f, 0x4f, 0x77, 0x32, 0xe9, 0xd6, 0x24, 0xc6, 0xc6, 0x15, 0x48, 0xab, 0x5f, 0xb8, 0xcd, 0x41, 0x02, 0x20, 0x18, 0x15, 0x22, 0xec, 0x8e, 0xca, 0x07, 0xde, 0x48, 0x60, 0xa4, 0xac, 0xdd, 0x12, 0x90, 0x9d, 0x83, 0x1c, 0xc5, 0x6c, 0xbb, 0xac, 0x46, 0x22, 0x08, 0x22, 0x21, 0xa8, 0x76, 0x8d, 0x1d, 0x09};
BITCOIN_ASSERT(signature.size() == 70);
elliptic_curve_key key;
if (!key.set_public_key(pubkey))
{
log_fatal() << "unable to set EC public key";
return -1;
}
log_info() << "checksig returns: " << (key.verify(tx_hash, signature) ? "true" : "false");
return 0;
}