Help:Installing Bitcoin Core: Difference between revisions
→Points to remember: added link to wallet page |
Typo: 'minted' -> 'mined'. Removed double spaces |
||
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
=== Generating === | === Generating === | ||
New coins are | New coins are mined through generating hashes. These generators are rewarded with a small fee for the computationally intensive task of incorporating your transactions into the block-chain. This fee halves each time 210000 blocks are added to the block chain, or approximately every 4 years. The fee will keep halving until it effectively reaches zero, at which point 21 million coins will be in circulation. | ||
[[Category:Introduction]] | [[Category:Introduction]] | ||
Revision as of 07:57, 22 June 2011
An account can effortlessly be created using an eWallet service. eWallet services provide an online wallet to hold your bitcoins.
This guide covers installing Bitcoin without needing a third party wallet service.
For Windows computers
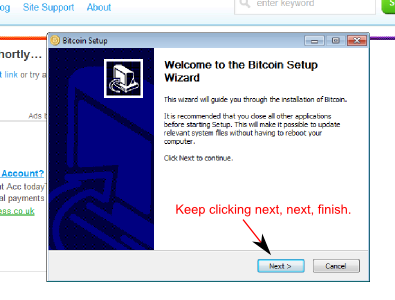
Installation
Download and install Bitcoin.
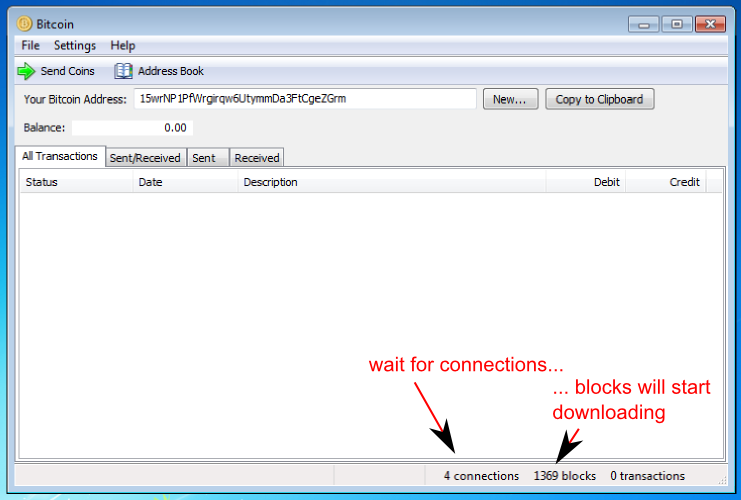
Initialization
The first time you run Bitcoin, it needs to download all the blocks to setup. You already have your bitcoin address at this point, but you won't see any transactions before the initialisation is complete (it can take from half to a few hours).
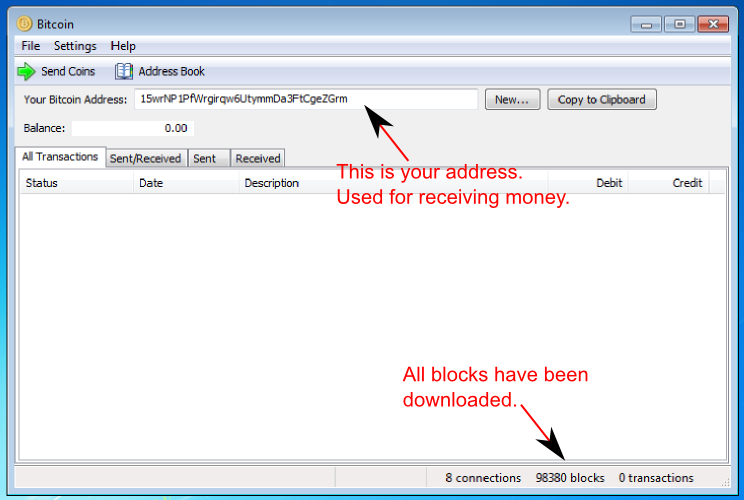
Your address (you can have as many as you want) is at the top. Below is your balance which will be zero. The list below shows your transactions.
For Mac computers
Download the OS X version of Bitcoin and expand the archive.
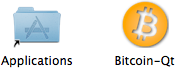
Drag the Bitcoin icon to the desired install location, and double-click or Cmd-O (⌘O) to run the application. The Bitcoin window will open and connections will start up in minutes. The blocks will begin downloading. Your address and balance are at the top of the window. Click "Copy to Clipboard" to copy your address. Transactions are displayed in the main window.
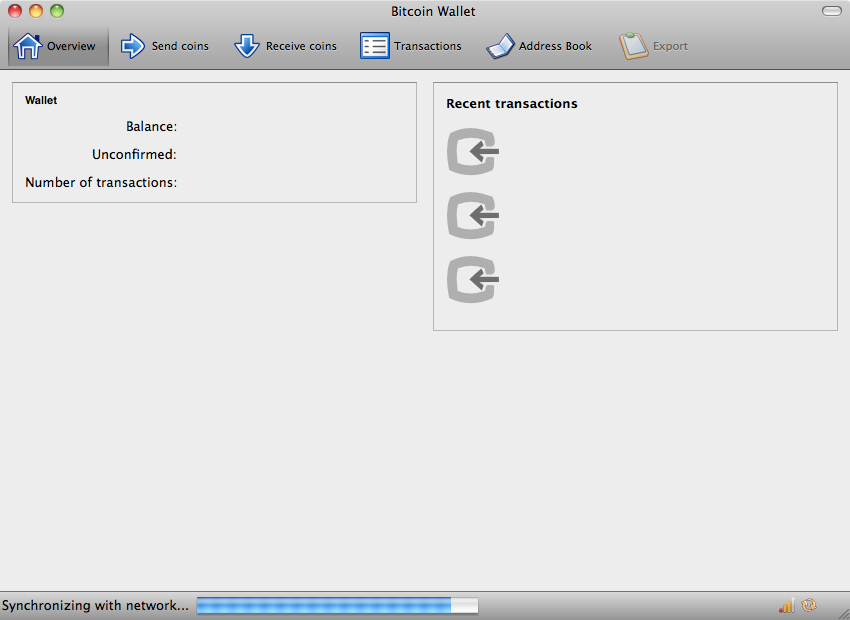
As Bitcoin currently does not support hiding with Cmd-H (⌘H), it is recommended that users tick the "Minimize on close" option in the Preferences menu to prevent accidental program exits.
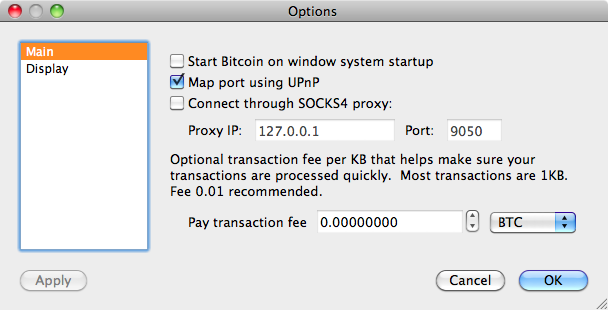
Getting my first coins
The Bitcoin Faucet website currently hands out 0.02 BTC to new bitcoin users. Fill in the form with your bitcoin address. When you wish to add more, view Buying bitcoins.

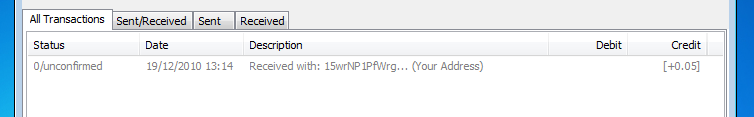
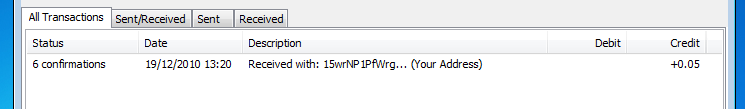
A new entry should appear in Bitcoin. The network hasn't yet confirmed it, but you know it's being processed. After about one hour it should get 6 confirmations. You are able to spend the coins when there is only one confirmation.
The confirmation counter (like the block counter) will increase by one roughly every 10 minutes. Six confirmations are considered as 100% sure a transfer has been processed.
- Play games and enter your first raffle at http://bitgames.jhfire.net!
- Create an account on witcoin and post something (cost 0.01 BTC):
http://www.witcoin.com (click "get wit it" to create an account)
If your post is any good, you can earn when it gets replies and votes. - Give a tip to a deserving artist, writer, etc. on YouTipIt.org.
For instance, this video creation is worth 0.05 BTC, no?:
http://www.youtipit.org/t/2652 - Give lady luck a shot?
Double Trouble (49% chance of doubling your money)
http://doubletrouble.bitcoinbet.com - Give to any of the charities on Bitcoin Trade page:
http://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Trade#Donation-accepting_organizations_and_projects
Points to remember
- You don't need to be online to receive BTC.
- You can create as many new addresses as you like. Using a different address each time helps keep you anonymous.
- You can be anonymous with adequate precautions.
- You cannot send BTC to an invalid address. Typos are not a worry as the payment will refuse to send.
- The wallet file holds the keys that allow spending and thus the computer should be protected from the risk of loss and theft.
- Leaving Bitcoin open improves connectivity for the network and ensures that you don't fall behind on the block chain. Also see the FAQ about port forwarding
Proceed to the introduction
Technical
Block chain
The block chain is a neverending story of every transaction throughout the network from day 1 (genesis). The first time you run Bitcoin, it is downloaded and verified on your computer. Every new transaction is added to the end of this chain and verified by the network to be valid.
Addresses
Whenever you send a coin, you are actually sending a cryptographically signed message, associating your coin with the recipient's address. This effectively transfers ownership to to the recipient. Once they own the coin, they are free to transfer it to another person.
A wallet is a collection of addresses. You can create as many new addresses as you wish; having more addresses makes you more anonymous, because then people cannot see how much BTC you received. Your wallet contains the secret keys used for spending that money, and must be backed-up regularly. If you lose the wallet then you no longer possess the money.
Generating
New coins are mined through generating hashes. These generators are rewarded with a small fee for the computationally intensive task of incorporating your transactions into the block-chain. This fee halves each time 210000 blocks are added to the block chain, or approximately every 4 years. The fee will keep halving until it effectively reaches zero, at which point 21 million coins will be in circulation.