Mining: Difference between revisions
Iamrichard (talk | contribs) |
Iamrichard (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
* [http://BitcoinMiner.net Comprehensive Guide Bitcoin Miner and Mining] | |||
* [http://codinginmysleep.com/bitcoin-mining-in-plain-english Bitcoin Mining in Plain English] by David Perry | * [http://codinginmysleep.com/bitcoin-mining-in-plain-english Bitcoin Mining in Plain English] by David Perry | ||
* [[Automatically mine when computer is locked|Tutorial to automatically start mining when you lock your computer]]. (Windows 7) | * [[Automatically mine when computer is locked|Tutorial to automatically start mining when you lock your computer]]. (Windows 7) | ||
Revision as of 20:10, 1 April 2014
Introduction
Mining is the process of adding transaction records to Bitcoin's public ledger of past transactions. This ledger of past transactions is called the block chain as it is a chain of blocks. The block chain serves to confirm transactions to the rest of the network as having taken place. Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to distinguish legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
Mining is intentionally designed to be resource-intensive and difficult so that the number of blocks found each day by miners remains steady. Individual blocks must contain a proof of work to be considered valid. This proof of work is verified by other Bitcoin nodes each time they receive a block. Bitcoin uses the hashcash proof-of-work function.
The primary purpose of mining is to allow Bitcoin nodes to reach a secure, tamper-resistant consensus. Mining is also the mechanism used to introduce Bitcoins into the system: Miners are paid any transaction fees as well as a "subsidy" of newly created coins. This both serves the purpose of disseminating new coins in a decentralized manner as well as motivating people to provide security for the system.
Bitcoin mining is so called because it resembles the mining of other commodities: it requires exertion and it slowly makes new currency available at a rate that resembles the rate at which commodities like gold are mined from the ground.
Difficulty
The Computationally-Difficult Problem
Mining a block is difficult because the SHA-256 hash of a block's header must be lower than or equal to the target in order for the block to be accepted by the network. This problem can be simplified for explanation purposes: The hash of a block must start with a certain number of zeros. The probability of calculating a hash that starts with many zeros is very low, therefore many attempts must be made. In order to generate a new hash each round, a nonce is incremented. See Proof of work for more information.
The Difficulty Metric
The difficulty is the measure of how difficult it is to find a new block compared to the easiest it can ever be. It is recalculated every 2016 blocks to a value such that the previous 2016 blocks would have been generated in exactly two weeks had everyone been mining at this difficulty. This will yield, on average, one block every ten minutes. As more miners join, the rate of block creation will go up. As the rate of block generation goes up, the difficulty rises to compensate which will push the rate of block creation back down. Any blocks released by malicious miners that do not meet the required difficulty target will simply be rejected by everyone on the network and thus will be worthless.
Reward
When a block is discovered, the discoverer may award themselves a certain number of bitcoins, which is agreed-upon by everyone in the network. Currently this bounty is 25 bitcoins; this value will halve every 210,000 blocks. See Controlled Currency Supply.
Additionally, the miner is awarded the fees paid by users sending transactions. The fee is an incentive for the miner to include the transaction in their block. In the future, as the number of new bitcoins miners are allowed to create in each block dwindles, the fees will make up a much more important percentage of mining income.
The mining ecosystem
Hardware
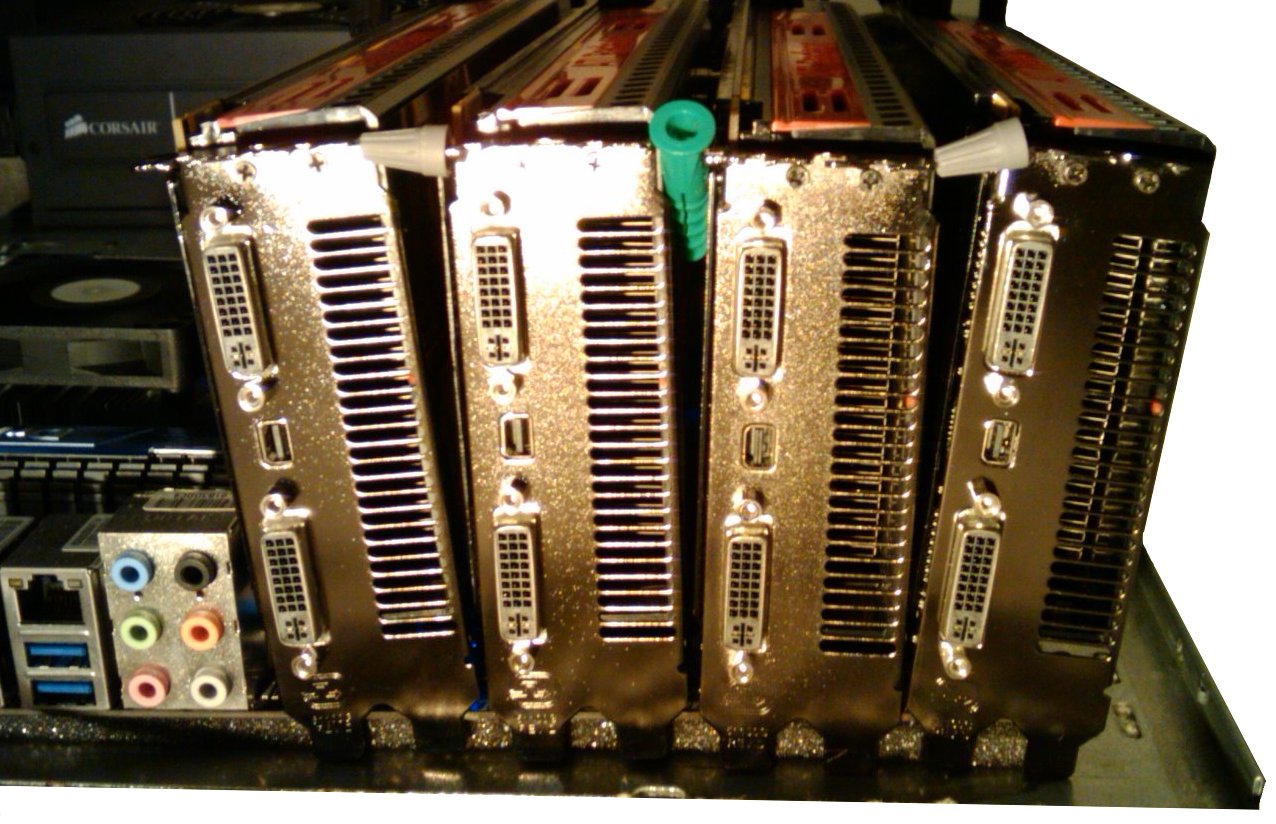
Users have used various types of hardware over time to mine blocks. Hardware specifications and performance statistics are detailed on the Mining Hardware Comparison page.
CPU Mining
Early Bitcoin client versions allowed users to use their CPUs to mine. As the network hashrate grew with more power efficient GPU miners the amount of Bitcoin's produced by CPU mining became lower than the cost of power to operate the CPUS. The option still exists in the reference Bitcoin client, but it is disabled by default.
GPU Mining
GPU Mining is drastically faster and more efficient than CPU mining. See the main article: Why a GPU mines faster than a CPU. A variety of popular mining rigs have been documented.
FPGA Mining
FPGA mining is a very efficient and fast way to mine, comparable to GPU mining and drastically outperforming CPU mining. FPGAs typically consume very small amounts of power with relatively high hash ratings, making them more viable and efficient than GPU mining. See Mining Hardware Comparison for FPGA hardware specifications and statistics.
ASIC Mining
An application-specific integrated circuit, or ASIC, is a microchip designed and manufactured for a very specific purpose. ASICs designed for Bitcoin mining were first released in 2013. For the amount of power they consume, they are vastly faster than all previous technologies and already has made GPU mining financially unwise in some countries and setups.
Cloud Mining
Instead of taking physical possession of a mining rig which can face additional costs and delays. Cloud mining is quickly becoming a better alternative. It allows you to 'rent' hashing power from another miner. It can be purchased on as little as an hourly basis thus allowing one to rent from anything from small scale rigs to industrial scale farms. A sample service is CEX.IO
Mining services
Mining contractors provide mining services with performance specified by contract. They may, for example, rent out a specific level of mining capacity for a set price for a specific duration.
Mining shares provide Mining as a Service (MaaS). These break large-scale datacenter mining down to easily manageable pieces that are available in the form of shares of equipment.
Hosted mining services create some systemic risk for the Bitcoin system because they undermine the security assumption that the control of mining power is well distributed. If too much mining becomes consolidated in large hosting providers and an attacker is able to compromise some of these providers they could potentially disrupt the Bitcoin system or rip off people they transact with with reversals.
Pools
As more and more miners competed for the limited supply of blocks, individuals found that they were working for months without finding a block and receiving reward for their mining efforts. This made mining something of a gamble. To address the variance in their income miners started organizing themselves into pools so that they could share rewards more evenly. See Pooled mining and Comparison of mining pools.
History
Bitcoin's public ledger (the 'block chain') was started on January 3rd, 2009 at 18:15 UTC presumably by Satoshi Nakamoto. The first block is known as the genesis block. The first transaction recorded in the first block was a single transaction paying the reward of 50 new bitcoins to its creator.