Mining: Difference between revisions
Rewrote some things |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<!-- This page is designed to be short and simple! It should provide only a very brief explanation of things that have their own page and should link to other pages whenever possible. This page should serve as an entry point and a place to organize most of our mining articles. Thank You! (-Atheros) --> | |||
[[File:Quick-and-dirty-4x5970-cooling.jpg|thumb|right|A quick and dirty mining rig]] | [[File:Quick-and-dirty-4x5970-cooling.jpg|thumb|right|A quick and dirty mining rig]] | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
'''Mining''' or generating, is the process of adding transaction records to Bitcoin's public ledger of past transactions. This ledger of past transactions is called the [[block chain]] as it is a chain of [[block|blocks]]. The block chain serves to [[Confirmation|confirm]] transactions to the rest of the network as having taken place. Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to distinguish legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to respend coins that have already been spent elsewhere. | |||
Mining is intentionally designed to be resource-intensive and difficult. Individual [[blocks]] must contain [[proof of work|proof of work]] | Mining is intentionally designed to be resource-intensive and difficult so that the number of blocks found each day by miners remains steady. Individual [[blocks]] must contain a [[proof of work|proof of work]] to be considered valid. This proof of work is verified by other Bitcoin nodes each time they receive a block. | ||
== History == | == History == | ||
Bitcoin's public | Bitcoin's public ledger (the 'block chain') was started on January 3rd, 2009 at 18:15 UTC presumably by [[Satoshi Nakamoto]]. The first block is known as the [[genesis block]]. The first transaction recorded in the first block was a single transaction paying the reward of 50 new bitcoins to its creator. | ||
Bitcoin mining is so called because the rate | Bitcoin mining is so called because it resembles the mining of other commodities: it requires exertion and it slowly makes new currency available at a rate that resembles the rate at which commodities like gold are mined from the ground. See [[Controlled Currency Supply]]. | ||
== Difficulty == | == Difficulty == | ||
| Line 21: | Line 19: | ||
=== Reward === | === Reward === | ||
When a block is discovered, the discoverer may award themselves a certain number of bitcoins, which is agreed-upon by everyone in the network. Currently this bounty is 50 bitcoins; this value will halve every 210,000 blocks. See [[Controlled Currency Supply]]. | When a block is discovered, the discoverer may award themselves a certain number of bitcoins, which is agreed-upon by everyone in the network. Currently this bounty is 50 bitcoins; this value will halve every 210,000 blocks. See [[Controlled Currency Supply]]. | ||
Additionally, the miner is awarded the fees paid by users sending transactions. The fee is an incentive for the miner to include the transaction in their block. In the future, as the number of new bitcoins miners are allowed to create in each block dwindles, the fees will make up a much more important percentage of mining income. | Additionally, the miner is awarded the fees paid by users sending transactions. The fee is an incentive for the miner to include the transaction in their block. In the future, as the number of new bitcoins miners are allowed to create in each block dwindles, the fees will make up a much more important percentage of mining income. | ||
| Line 36: | Line 34: | ||
=== Mining in the Future === | === Mining in the Future === | ||
In December 2012 the block reward is expected to reduce from 50 BTC per block to 25. | In December 2012 the block reward is expected to reduce from 50 BTC per block to 25. If and only if the value of each bitcoin remains constant between now and then, miners will lose 50% of their revenue. An upwards trend of [[difficulty]] is expected through 2012 towards December with the expected advent of ASICs and efficient FPGAs adding to overall network mining capacity. GPU mining is expected to reach a peak in growth and to slowly decline in the future. | ||
== Pools == | == Pools == | ||
As mining a block became more and more difficult, individuals found that they were working for months without finding a block and receiving ''any'' reward for their mining efforts. Thus they started organizing themselves into [[Pooled mining|pools]] so that they could share rewards more evenly. See [[Pooled mining]] and [[Comparison of mining pools]]. | As mining a block became more and more difficult, individuals found that they were working for months without finding a block and receiving ''any'' reward for their mining efforts. Thus they started organizing themselves into [[Pooled mining|pools]] so that they could share rewards more evenly. See [[Pooled mining]] and [[Comparison of mining pools]]. | ||
[[Category:Mining]][[Category:Vocabulary]] | [[Category:Mining]][[Category:Vocabulary]] | ||
Revision as of 16:31, 28 August 2012
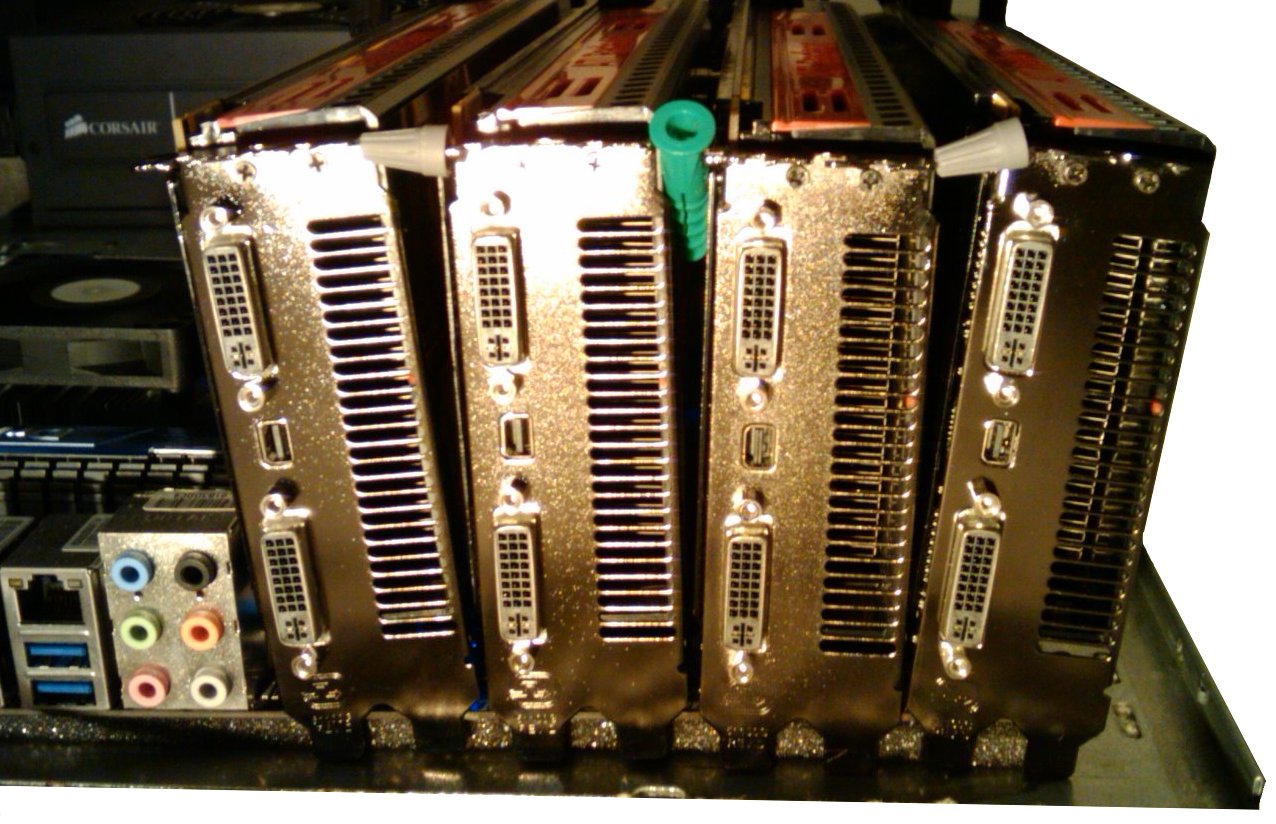
Introduction
Mining or generating, is the process of adding transaction records to Bitcoin's public ledger of past transactions. This ledger of past transactions is called the block chain as it is a chain of blocks. The block chain serves to confirm transactions to the rest of the network as having taken place. Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to distinguish legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to respend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
Mining is intentionally designed to be resource-intensive and difficult so that the number of blocks found each day by miners remains steady. Individual blocks must contain a proof of work to be considered valid. This proof of work is verified by other Bitcoin nodes each time they receive a block.
History
Bitcoin's public ledger (the 'block chain') was started on January 3rd, 2009 at 18:15 UTC presumably by Satoshi Nakamoto. The first block is known as the genesis block. The first transaction recorded in the first block was a single transaction paying the reward of 50 new bitcoins to its creator.
Bitcoin mining is so called because it resembles the mining of other commodities: it requires exertion and it slowly makes new currency available at a rate that resembles the rate at which commodities like gold are mined from the ground. See Controlled Currency Supply.
Difficulty
The Computationally-Difficult Problem
Mining a block is difficult because the SHA-256 hash of a block's header must be lower than or equal to the target in order for the block to be accepted by the network. This problem can be simplified for explanation purposes: The hash of a block must start with a certain number of zeros. The probability of calculating a hash that starts with many zeros is very low, therefore many attempts must be made. In order to generate a new hash each round, a nonce is incremented. See Proof of work for more information.
The Difficulty Metric
The difficulty is the measure of how difficult it is to find a new block compared to the easiest it can ever be. It is recalculated every 2016 blocks to a value such that the previous 2016 blocks would have been generated in exactly two weeks had everyone been mining at this difficulty. This will yield, on average, one block every ten minutes. As more miners join, the rate of block creation will go up. As the rate of block generation goes up, the difficulty rises to compensate which will push the rate of block creation back down. Any blocks released by malicious miners that do not meet the required difficulty target will simply be rejected by everyone on the network and thus will be worthless.
Reward
When a block is discovered, the discoverer may award themselves a certain number of bitcoins, which is agreed-upon by everyone in the network. Currently this bounty is 50 bitcoins; this value will halve every 210,000 blocks. See Controlled Currency Supply.
Additionally, the miner is awarded the fees paid by users sending transactions. The fee is an incentive for the miner to include the transaction in their block. In the future, as the number of new bitcoins miners are allowed to create in each block dwindles, the fees will make up a much more important percentage of mining income.
Making a Profit
Hardware
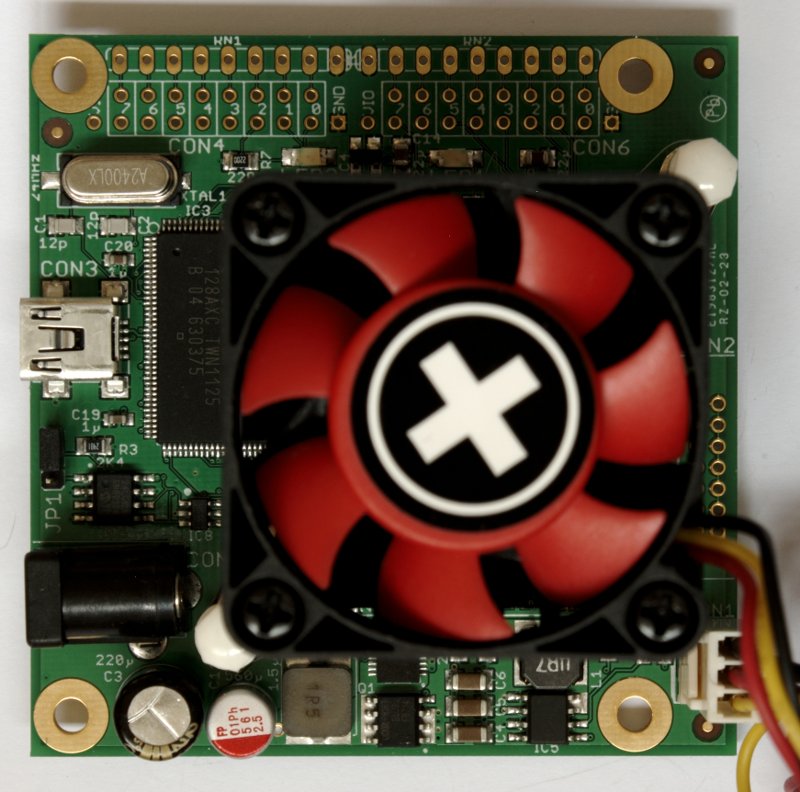
Users have used various types of hardware over time to mine blocks. Hardware specifications and performance statistics are detailed on the Mining Hardware Comparison page.
CPU Mining
Early Bitcoin client versions allowed users to use their CPUs to mine. The advent of GPU mining made CPU mining financially unwise. The option was therefore removed from the Bitcoin client.
GPU Mining
GPU Mining is drastically faster and more efficient than CPU mining. See the main article: Why a GPU mines faster than a CPU. A variety of popular mining rigs have been documented.
FPGA Mining
FPGA mining is a very efficient and fast way to mine, comparable to GPU mining and drastically outperforming CPU mining. FPGAs typically consume very small amounts of power with relatively high hash ratings, making them more viable and efficient than GPU mining. See Mining Hardware Comparison for FPGA hardware specifications and statistics.
Mining in the Future
In December 2012 the block reward is expected to reduce from 50 BTC per block to 25. If and only if the value of each bitcoin remains constant between now and then, miners will lose 50% of their revenue. An upwards trend of difficulty is expected through 2012 towards December with the expected advent of ASICs and efficient FPGAs adding to overall network mining capacity. GPU mining is expected to reach a peak in growth and to slowly decline in the future.
Pools
As mining a block became more and more difficult, individuals found that they were working for months without finding a block and receiving any reward for their mining efforts. Thus they started organizing themselves into pools so that they could share rewards more evenly. See Pooled mining and Comparison of mining pools.