Difference between revisions of "Libbitcoin Blockchain"
m (Add database files list.) |
m |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==Example== | ==Example== | ||
| − | + | #include <string> | |
| − | + | #include <bitcoin/blockchain.hpp> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | // Initialize the blockchain | |
| − | + | int main(int argc, char* argv[]) | |
| − | + | { | |
| − | + | std::string prefix("blockchain"); | |
| + | |||
| + | if (argc > 1) | ||
| + | prefix = argv[1]; | ||
| − | + | bc::chain::initialize_blockchain(prefix); | |
| − | + | bc::chain::db_paths paths(prefix); | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | constexpr size_t history_height = 0; | |
| − | + | bc::chain::db_interface interface(paths, { history_height }); | |
| − | + | interface.start(); | |
| − | + | const auto genesis = bc::genesis_block(); | |
| − | + | interface.push(genesis); | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | return 0; | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Design== | ==Design== | ||
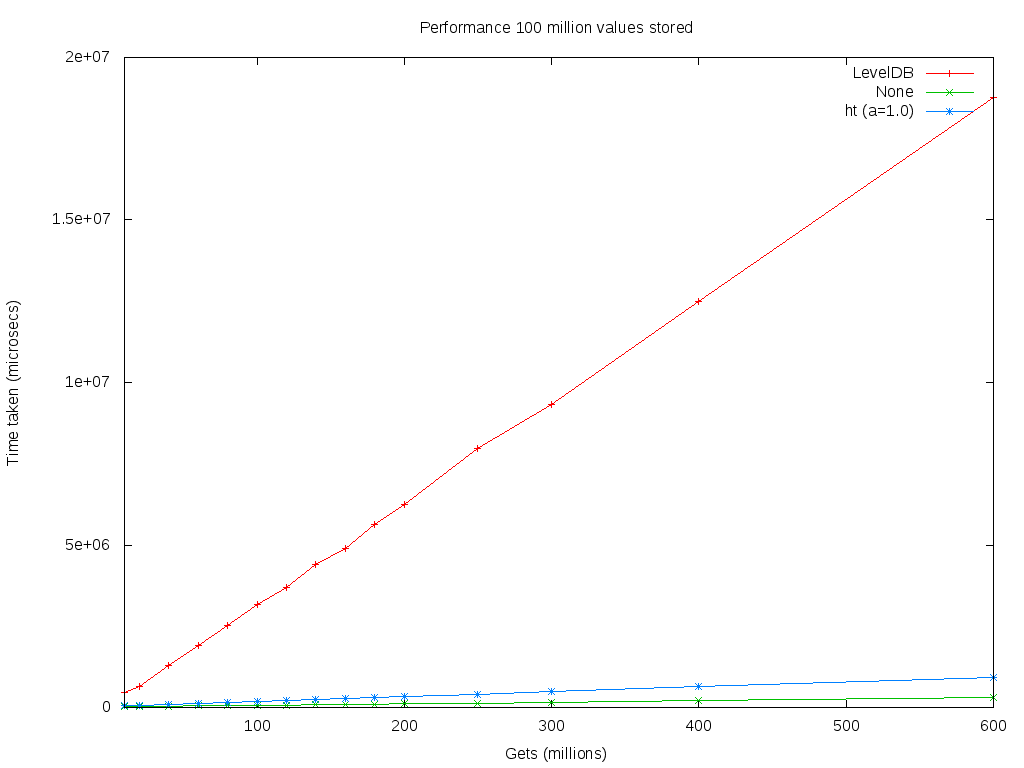
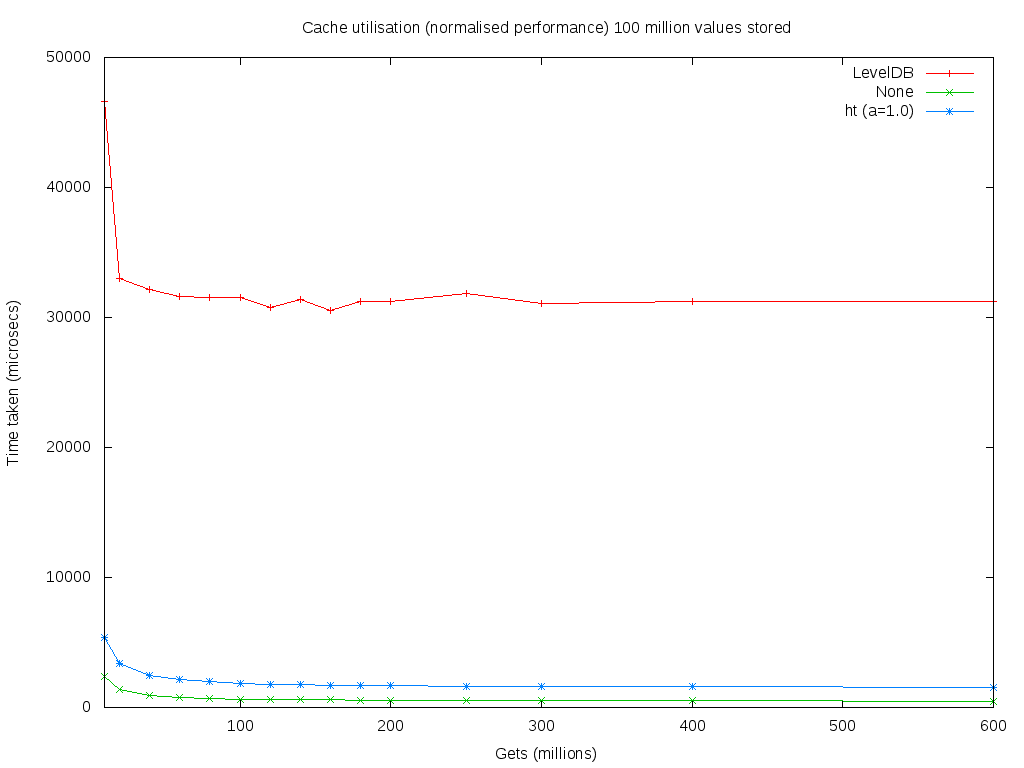
| − | The original implementation used [http://leveldb.org LevelDB]. Following a redesign in late 2014 by [[Amir_Taaki|Amir Taaki]] (genjix) the database was replaced by a memory-mapped I/O implementation. Logical queries are performed using a set of hash tables. The number of hash buckets is optimized to minimize hash collisions, though collisions are accommodated. These changes resulted in a substantial performance increase for queries against the blockchain. Insert performance | + | The original implementation used [http://leveldb.org LevelDB]. Following a redesign in late 2014 by [[Amir_Taaki|Amir Taaki]] (genjix) the database was replaced by a memory-mapped I/O implementation. Logical queries are performed using a set of hash tables. The number of hash buckets is optimized to minimize hash collisions, though collisions are accommodated. These changes resulted in a substantial performance increase, near constant time, for queries against the blockchain. Insert performance was not materially affected. |
[[Image:Libbitcoin-blockchain-gets.png|500px]] [[Image:Libbitcoin-blockchain-gets-normalised.png|500px]] | [[Image:Libbitcoin-blockchain-gets.png|500px]] [[Image:Libbitcoin-blockchain-gets-normalised.png|500px]] | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
* stealth_rows | * stealth_rows | ||
* txs | * txs | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Consensus Validation== | ||
| + | By default the library depends on the [[Libbitcoin_Consensus|libbitcoin-consensus]] library. This ensures that consensus checks are identical to those implemented by [[Bitcoind|bitcoind]]. By building using the ''--without-consensus'' flag the dependency is avoided and [[Libbitcoin|libbitcoin]] native consensus checks are used instead. | ||
==Considerations== | ==Considerations== | ||
Revision as of 06:14, 14 May 2015
The libbitcoin-blockchain library is a dependency of libbitcoin-node and libbitcoin-server. It was originally contained within libbitcoin.
Contents
Example
#include <string>
#include <bitcoin/blockchain.hpp>
// Initialize the blockchain
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
std::string prefix("blockchain");
if (argc > 1)
prefix = argv[1];
bc::chain::initialize_blockchain(prefix);
bc::chain::db_paths paths(prefix);
constexpr size_t history_height = 0;
bc::chain::db_interface interface(paths, { history_height });
interface.start();
const auto genesis = bc::genesis_block();
interface.push(genesis);
return 0;
}
Design
The original implementation used LevelDB. Following a redesign in late 2014 by Amir Taaki (genjix) the database was replaced by a memory-mapped I/O implementation. Logical queries are performed using a set of hash tables. The number of hash buckets is optimized to minimize hash collisions, though collisions are accommodated. These changes resulted in a substantial performance increase, near constant time, for queries against the blockchain. Insert performance was not materially affected.
Database
The following files constitute the blockchain database non-volatile storage. As of height 350,000 the database consumes approximately 105 GB of disk space.
- blocks_lookup
- blocks_rows
- history_lookup
- history_rows
- spends
- stealth_index
- stealth_rows
- txs
Consensus Validation
By default the library depends on the libbitcoin-consensus library. This ensures that consensus checks are identical to those implemented by bitcoind. By building using the --without-consensus flag the dependency is avoided and libbitcoin native consensus checks are used instead.
Considerations
- There is no mechanical hard drive optimization. The implementation is intended for solid state drives (SSD).
- There is a possibility of index corruption during hard shutdown. There is no means of detecting corruption aside from catastrophic fault. However given that the entire blockchain is a cache this is not considered significant. Repair can be accomplished by re-synchronizing the blockchain.
- Data files are append only, with logical deletions only. Therefore file size is not minimized following blockchain reorganization although the impact is typically small. Defragmentation can be accomplished by re-synchronizing the blockchain.
- The database is effectively locked during write operations. As these operations are anticipated on a period of approximately ten minutes this is not typically significant. However during a period of catch-up synchronizing the server can become continuously unresponsive to requests.
Dependencies
- boost
- libsecp256k1
- libbitcoin-consensus (optional)